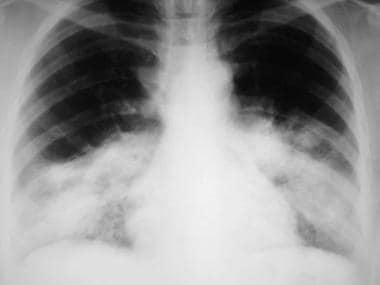
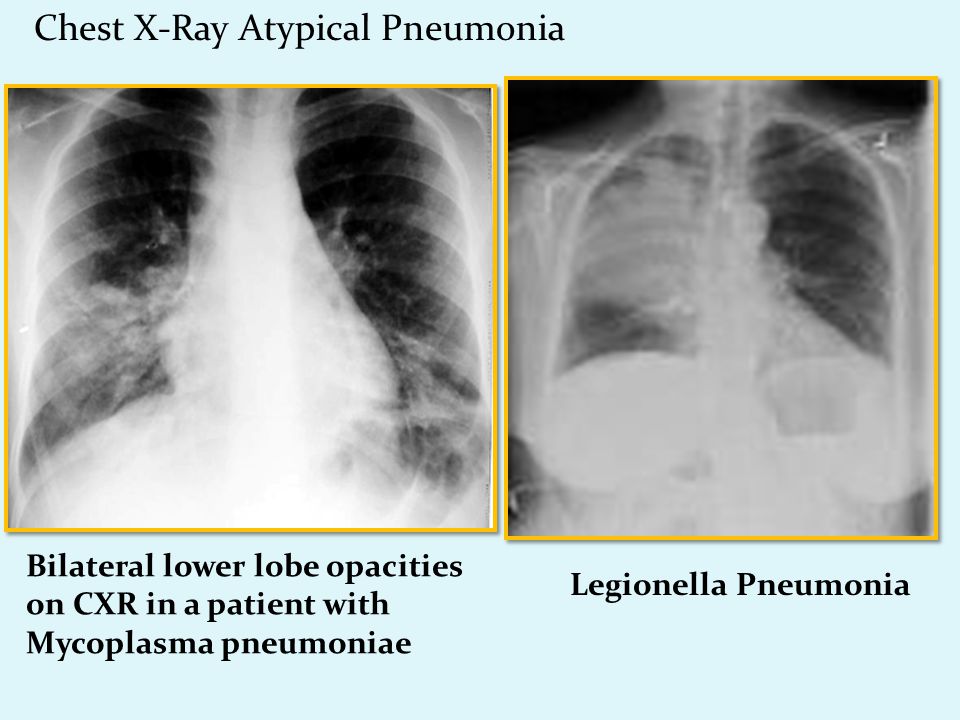
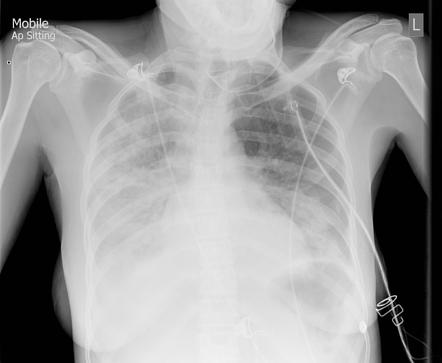
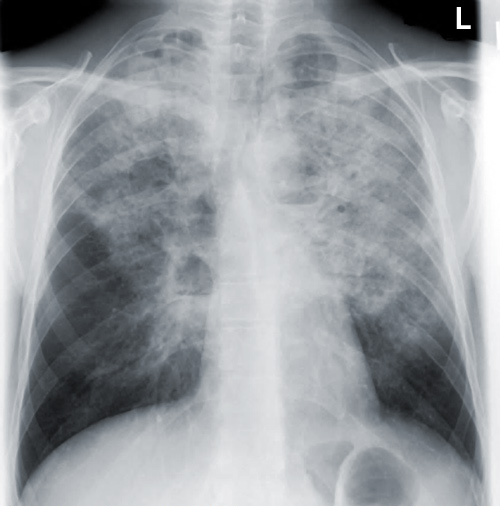
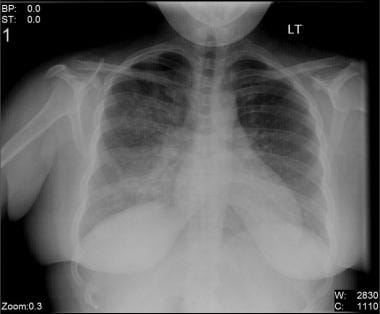
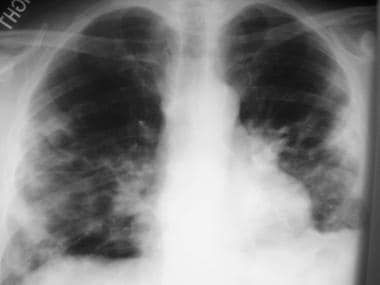
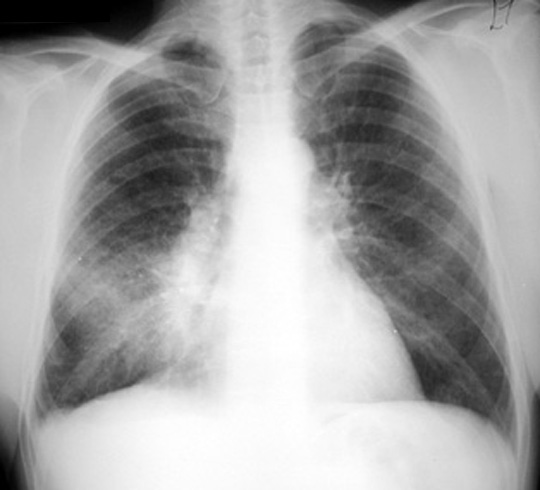
Bilateral Atypical Pneumonia

Involvement is often diffuse and bilateral 9.
Bilateral atypical pneumonia. Chlamydophila pneumoniae is common in school aged children and. Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs. Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs that can be caused by viruses bacteria and fungi. Learn the warning signs who.
However some families of bacteria can affect both lungs. Its clinical presentation contrasts to that of typical pneumonia. Three specific infectious bacteria cause the majority of atypical pneumonia cases. The infection inflames the air sacs in your lungs or the alveoli which fill with fluid or pus.
Legionnaires disease it is atypical pneumonia caused by bacterium legionella. The reasons for the development of bilateral pneumonia bilateral pneumonia is often triggered by the influence of harmful microorganisms in the lung tissue. Pneumonia caused by pseudomonas or by staphylococcus after flu is often bilateral. A severe type.
When it develops independently from another disease it is called primary atypical pneumonia pap. Bilateral pneumonia causes bacteria usually bacteria affect only a part of one lung. Bilateral pneumonia is one of the most dangerous diseases of the lungs which if improper treatment can result in death of the patient. It commonly causes earaches headaches and a sore throat as.
This lung illness may cause severe breathing problems that put you in the hospital. The air sacs may fill with fluid or pus purulent material causing cough with phlegm or pus fever chills and difficulty breathing. A variety of microorganisms can cause it. These bacteria are referred to as atypical.
Mycoplasma pneumoniae usually infects people under 40 with mild pneumonia symptoms. This inflammation makes it. Bronchial wall thickening is another common ct finding 6. Atypical pneumonia has a pattern of focal ground glass opacity in a lobular distribution.
Atypical pneumonia also known as walking pneumonia is any type of pneumonia not caused by one of the pathogens most commonly associated with the disease. Viral pneumonia of viral cause can affect both lungs. There may also be evidence of pleural effusion. Double pneumonia is a lung infection that affects both of your lungs.
Bacteria that can cause pneumonia include mycoplasma pneumoniae chlamydophila chlamydia pneumoniae chlamydophila chlamydia psittaci and legionella pneumophila.